
Ever since paper was invented in ancient China about 2,000 years ago, it has become a part of our everyday life. Used primarily for writing and then printing, modern applications of paper are manifold and versatile and constitute a chunk of today’s financial, business and professional, individual, communication, documentation, and artistic works, besides industrial uses for packaging, cleaning, food utensils and containers, construction, etc.
Paper Consumption in the Modern World
In the modern scenario, paper consumption is a global phenomenon that has been on the rise for decades. The increasing demand for paper products has led to a significant increase in the amount of paper produced and consumed worldwide. However, in recent years, there have been some shifts in paper consumption trends that are worth noting.
One trend that has become increasingly apparent is a shift away from traditional paper products such as books and newspapers towards digital alternatives. The rise of e-books and online news sources has led to a decrease in the demand for traditional paper products, causing a decline in overall paper consumption. Additionally, many businesses and organisations are also shifting towards digital alternatives for their internal and external communications, which has further reduced paper consumption.

Another tendency that has emerged in recent years is an increase in the demand for recycled paper. As awareness of the environmental impacts of paper production has grown, consumers and organisations have become more conscious of the impact of their paper consumption. This has led to an increase in the demand for recycled paper, which is considered to be a more sustainable option than virgin paper.
The paper consumption varies among different regions and countries. According to the World Bank data, the highest paper consumption per capita is in North America with around 606 kg per person followed by Europe with around 480 kg per person. However, it is worth noting that these figures are for all paper products and do not take into account the shift towards digital alternatives.
In conclusion, paper consumption is a global phenomenon that is affected by a variety of factors. While overall paper consumption has been on the rise for decades, there are some trends that suggest a shift away from traditional paper products and towards digital alternatives and recycled paper. These trends are likely to continue to shape the paper industry in the years to come.
Paper vs. Digital
Digital media has come a long way in recent years and has become an integral part of our daily lives. From smartphones and tablets to laptops and e-readers, digital devices have made it easier than ever to access and consume information. However, despite the advancements in digital technology, it is unlikely that paper will be replaced by digital media any time soon.
One of the main reasons why paper will not be replaced by digital media is that paper has certain advantages that digital media cannot replicate. For example, paper is a tangible medium, which means that it can be physically touched and handled. This makes it ideal for reading and studying, as it is easier to focus on the text and make notes. Additionally, paper is also a more durable medium than digital media and is less likely to be damaged by water or other environmental factors.
Another reason why paper will not be replaced by digital media is that paper is still an essential medium for many industries. For example, the printing and publishing industry relies heavily on paper, as do other industries such as packaging, education, and healthcare. Many of the printed materials such as textbooks, medical records, and legal documents still need to be in paper format.
Additionally, since paper has a certain appeal and nostalgia that digital media cannot replicate, right from the smell of a new book to the tactile sensation of flipping through its pages, many people still enjoy reading physical books, magazines, and newspapers.
Lastly, there is also a segment of populations that do not have access to digital media or lack the technological literacy. For example, in rural areas or underprivileged communities, many people do not have access to the internet or digital devices, making paper the only option for accessing information.
On the whole, while digital media has made significant strides in recent years, it is unlikely that it will replace paper any time soon. Paper has certain advantages and is still an essential medium for many industries and individuals. While digital media is convenient and accessible, it cannot replace the tactile and aesthetic experience that paper provides.
Global Paper Industry
The world’s top paper producing countries and the largest paper companies play a vital role in the growth of the global pulp and paper industry, and produce some of the most important materials that are used on a daily basis for several commercial and domestic purposes. The market for paper and paper products is expected to grow at a steady rate globally over the next few years, mainly driven by the rising demand in downstream sectors such as printing, consumer packaging, pharmaceutical, construction, etc. Despite the challenges faced by the pulp and paper industry with environmental pressures to reduce the volume and toxicity of its industrial wastewater, the world’s top 10 largest paper companies and leading paper producing countries are still projected to have strong growth in their paper productions and revenues over the next few years.
The global paper industry is a thriving business recording huge production and consumption around the world. According to an estimate by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, the global production of paper and paperboard was around 490 million tons in 2020. A recent market research by Reports and Data, the global paper and pulp market size, valued at $518.83 billion in 2019 is expected to reach $679.72 billion by the year 2027, at a CAGR of 3.45% during the forecast period.
Packaging is the largest consuming sector in the global paper industry; with over 52% of the world’s paper production being used as packaging paper, while almost 33% is used as graphic paper for printing purposes. The growth of the consumer product packaging sector will be driven largely by demographic shifts and consumer trends such as the demand for convenience and sustainability, as well as the rising concerns over plastic packaging waste. As a result, the global paper industry is expected to be further boosted by the rising demand of the paper packaging segment in the near future.

Geographically, Asia-Pacific accounts for the largest market share in the global paper and pulp market. This is mainly attributed to the fact that China, Japan, and South Korea are some of the world’s largest paper producing countries and top paper consumers with some of the highest demand in their paper packaging industry. Goldstein Research reports that the Asia-Pacific region is expected to hold 34% revenue share of global paper and paper packaging market in 2024.
China, the World’s Largest Paper Producer and Consumer
According to market data provider Statista, the global paper and paperboard production surpassed 417 million metric tons in 2021, which was an increase of roughly 4% from the previous year. China is the world’s largest paper producer by far, with a production output of 125 million metric tons in 2021, followed by the United States, and Japan. These top three countries account for over 50% of the world’s total annual paper production. Other nations in the list include Germany, South Korea, Finland, Brazil, Canada, Sweden, and Italy, with Germany and the United States as the top two leading paper importing and exporting countries.

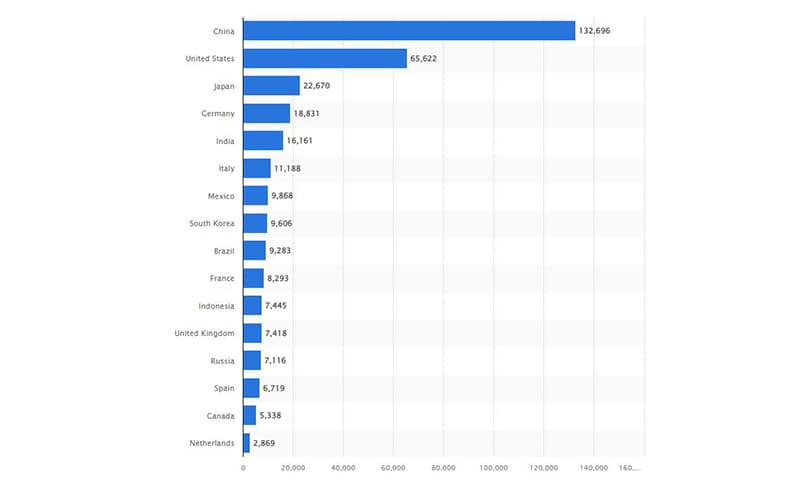
The global consumption of paper and paperboard totaled 408 million tons in 2021, with consumption projected to rise over the coming decade to reach 476 million tons by 2032. China is the world’s largest consumer of paper and paperboard by far, consuming 132.7 million metric tons worth in 2021. This was roughly the combined quantity of paper and paperboard consumed in the United States, Japan, Germany, India, and Italy, and accounted for 32% of global paper and paperboard consumption in 2021. Completing the top 10 consumers are Mexico, South Korea, Brazil, and France.
Germany emerges Top Exporter of Paper in 2021
Though China is the largest producer of paper and paperboard, Germany emerged as the top exporter in 2021, with shipments totaling 14.7 million metric tons, followed by the United States, Sweden, and Finland.
US-company Tops Global Forestry and Paper Company Revenue
American pulp and paper company International Paper emerged as the world’s largest forestry and paper company in 2021 generating revenue of over $19 billion. Japan’s Oji Holdings and Finland’s Stora Enso were placed second and third with revenues of over $12 million and $11 million, respectively. Other leading players not far behind in the lucrative market are Finland’s UPM-Kymmene, Canada’s West Fraser Timber, and Hong Kong’s Nine Dragons Paper.
Future Trends of the Global Paper Industry
The rapid shift towards sustainable paper production and recyclable feature of paper and packaging products have become some of the major paper industry trends over the recent years. These trends are mainly driven by the rising consumer awareness about non-biodegradable materials and its effect on the environment. Many of the world’s largest paper companies and leading paper product manufacturers have invested heavily in sustainable production and the adoption of eco-friendly materials. These will also be some of the key factors which are boosting the growth of the global paper industry in the near future.
Paper Industry in the Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa pulp and paper market is expected to reach a CAGR of 3.2% during the forecast period (2021-2026), owing to rapid changes in the lifestyle, an increase in consumer demand for packaged and fresh food, and presence of a relatively young population are some of the major drivers impacting the growth of paper packaging, thus raising the growth opportunities for the pulp market in the region. The outbreak of COVID-19 had negatively impacted this market initially with some of the effects of lockdowns including disruption in supply chains, lack of availability of raw materials used in the manufacturing process, labour shortages, fluctuating prices, blank sailings and port closures, etc.
The UAE has emerged as the biggest in annual per capita expenditure in the MENA region at $1,648 per online shopper. With the exponential growth in e-commerce, the UAE’s packaging market is expected to touch $6,193.16 million during 2021-2026 from $2,813.5 million in 2020, at a CAGR of 4.6%.
In Saudi Arabia, paper and paperboards marketing is expected to touch $2,625 million during 2022-2027, at a CAGR of 4.31%. The Kingdom has also witnessed robust growth in its retail ready packaging (RRP) business, with packaged food sales estimated at $20 billion in 2021.
Key Market Trends in the MEA region
The cosmetic industry is expected to drive the growth of the market. The UAE and Saudi Arabia are estimated to motivate the demand for cosmetic products during the forecast period (2021-2026) owing to the growing demand for halal cosmetic products, and this in turn has created an upsurge in demand for manufacture of cosmetic packaging.
Consumers in the UAE are spoilt for choice in terms of cosmetics and fragrances. To capture the maximum share market and enhance their market presence, beauty and fragrance companies are keeping their packaging sustainable, convenient, and exciting. A variety of innovative and sustainable solutions including smart usage, handy grab-and-go, preservation-enhancing packs; reusable packaging, popularized by the refill revolution; recyclable sachets; and easy-to-open designs are all being tailor-made for the growing list of on-the-go, demanding customers.
Total revenues in the UAE beauty and personal care market was around $1.3 billion in 2022, with 24% coming from e-commerce channels.
Luxury packaging is an area seeing a boom in the MEA region. Recent trends driving the market include bio-degradable and sustainable packaging. It is forecast that the market value of luxury packaging in the MEA region will increase to nearly $1.2 billion by 2025.
Africa is Expected to Witness Significant Growth
South Africa has witnessed high levels of urbanization over the last few years. As per a recent study, around 64% of South Africans are living in urban areas, and this is expected to rise to 71% by 2030. By 2050, eight in ten people are expected to live in urban areas.
As urbanization is picking up, cities like Johannesburg, Cape Town, and Durban are attracting a younger generation of consumers, who are changing their consumption habits and are increasingly buying processed and packaged foods. This also creates more demand for ready or on-the-go meals, which directly drive the demand for pulp and paper-based packaging and products such as tissue papers.
Moreover, South Africa is in the enviable position of being able to recycle up to 90% of its recovered waste paper locally into paper packaging, serving the agricultural, manufacturing, and retail sectors.
Market players have begun to adopt the latest technologies and machinery to expand their presence in the regional market. Moreover, the growing public-private partnerships (PPPs) in the region are expected to boost the market growth. Ghana is expected to produce its paper by establishing a pulp mill to boost the paper industry in the country and also for export to the West African sub-region. The $2.8 billion dollar PPP project between the government of Ghana and Swedish paper company Greenland Resources AB is expected to produce 1.5 million tons of pulp and paper annually to feed the paper industry in the country.
Paper Shortage and Spiraling Prices
Paper shortages and the resulting price increases have had a significant impact on the printing and publishing industry. The industry relies heavily on paper as a raw material, and the recent shortages and price hikes have led to increased costs for manufacturers, which in turn have been passed on to consumers in the form of overpriced printed materials.
One of the major factors contributing to the paper shortage is a decrease in demand due to the shift towards digital media. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to disruptions in global supply chains, making it more difficult for paper producers to meet global demands.
Realising these predicaments, major paper producers have implemented a variety of strategies to mitigate paper shortages and price increases, such as increasing production, reducing waste, and investing in new technologies to improve efficiency.
While Memphis-headquartered International Paper has invested in new production facilities and equipment to increase capacity, and has implemented recycling programmes to reduce waste, others have focused on reducing costs by implementing new technologies, automating production processes, and shifting their focus to higher-margin products, such as packaging materials, in order to mitigate the impact of paper shortages and price increases on their bottom line.
Despite these efforts, the paper shortages and price increases are likely to continue to be a major challenge for the printing and publishing industry in the short term. The industry will need to adapt to the changing market conditions, such as by investing in digital technologies and alternative materials, in order to remain competitive in the long term.
Paper Shortage and Plans for the Future
Looking ahead, many marketing businesses and printers are planning ahead and ordering more paper to prepare for the continued shortage that according to industry experts, is expected to stay the same through the end of 2023. These speculative bulk purchases have contributed to the current paper shortage and impacted the printing industry for the rest of the year.
Market leaders hope that by the end of 2023 or early 2024, things may level out thanks to reduced demands and an increase in paper supply. However, the current uncertainty surrounding the paper market makes predictions about future outcomes difficult.





